The Function of computer hardware components (P1)
The Function of computer hardware components (P1)
Task (P1)
Task (P1)
Internal System Unit: Processors
Definition: A processor is an integrated electronic circuit
that make a as a job of it performs that the calculations make a run on a
computer.
The Functions of the Processor:
- Fetch: each of the data instruction are
stored in a memory and it has own of the address. The processor will take
this number from the address itself then proceed to the program counter,
which is make its a responsible for tracking of the data that is stored
from the memory which instructions of the CPU should make an execute next.
- Decode: All the programs that is process by
the CPU will made to be executed and translated into an Assembly
instruction. The assembly code must be decoded and breaking the codes into
a binary instruction, which is to make understandable to your CPU. (Decoding)
- Execute: during the executing while making
an executing of the instructions to the CPU can made it into 3 things.
1.
Do the calculations with its ALU (Arithmetic
Logic Unit)
2.
move the data from one memory location to
another
3.
jump to a different address.
- Store: The CPU must give a feedback after the processing of Fetch, Decode, Executing an instruction, and the output data is written itself and save it to the memory.
 |
| Diagram 1: The Processor |
Definition: The motherboard is a printed circuit board and foundation of
a computer that is the biggest board in a computer chassis. It allocates power
and allows communication to and between the CPU, RAM, and all other computer
hardware components.
Functions of Motherboards:
1.
The motherboard is job as a central backbone of a computer.
which the other modular parts are installed for example the CPU, RAM and hard
disks.
2.
The motherboard also makes its job as the platform on which
various expansion slots are available to install other devices / interfaces.
3.
The motherboard is also responsible to distribute the power to
other components inside the computer. They are also has to make is a used of
the coordination from the various devices in the computer and maintain an
interface among them.
 |
| Diagram 2: Motherboard
Internal System Unit: BIOS
Definition: Basic Input Output System. It is software stored
on a small memory chip on the motherboard.
Functions of BIOS:
1.
POST. - The first and foremost function of BIOS is to
make sure that the computer hardware is functioning properly and there is no
issue with the hardware. This is done by the Power on Self-Test (POST). If the
POST test fails computer generates different types of beeps to indicate the
type of error. If the POST test is passed then booting starts.
2.
Booting. - After the successful complete on POST, The BIOS
will locate and identifies the operating system. The BIOS then passes the
control to the Operating system to find its one. Then it is automatically boot
up.
3.
BIOS Driver. - This is were the collection of programs
that are stored in the non-volatile erasable memory chips, The BIOS Drivers gives
basic information about computer hardware.
4.
BIOS Setup. - It is a configuration program that permits us to
configure hardware settings. BIOS setup is also known as CMOS setup
|
 |
| Diagram 3: BIOS |
Definition: A power supply is a component
that supplies power to at least one electric load. Typically, it converts one
type of electrical power to another, but it may also convert a a different form
of energy.
Functions: A power supply provides components with
electric power. The term usually pertains to devices integrated within the
component being powered. For example, computer power supplies convert AC
current to DC current and are generally located at the rear of the computer
case, along with at least one fan.
 |
| Diagram 4: Power Supply |
Internal system unit: Heatsink and cooling fan
Definition: A heat sink and fan (HSF) is an active
cooling solution used to cool down integrated circuits in computer systems,
commonly the central processing unit (CPU). The heat sink is usually made from
a high-temperature conductive material such as aluminum and copper, and the fan
is a DC brushless fan
Internal system unit: Hard drive
Functions:
To cooldown the CPU from distinctive heat.
| Diagram 5: Heatsink and Cooling Fan |
Functions:
It
is an exclusively for store the data. this
is where the data are automatically transfer it . and it can act as emergency
boot drive which can be used for regular/irregular data backup.
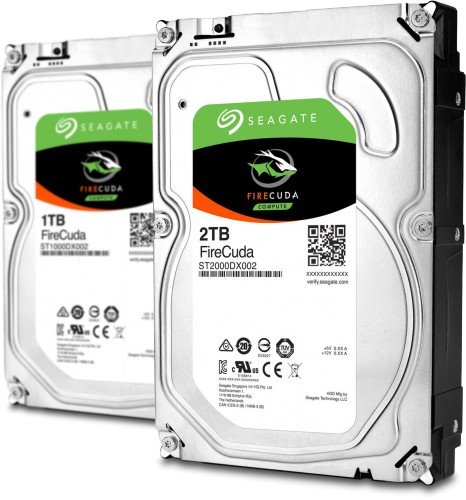 |
| Diagram 6: Hard Drive |
Internal system unit: Controllers
IDE
Definition: IDE
means Integrated Drive Electronics, it is a standard electronic interface used
between a computer motherboard’s data paths or bus and the computer's disk
storage devices.
Functions: the
IDE controller is often built into the motherboard. Prior to the IDE drive,
controllers were separate external devices so IDE reduced problems associated
with storage devices and integrated controllers.
EIDE
Definition: Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics.
Functions: EIDE
is an improved version of the IDE drive interface that provides faster data
transfer rates than the original standard. EIDE can transfer data up to 16.6
Mbps
 |
| Diagram 7: IDE and EIDE |
Definition: Serial
Advanced Technology Attachment known as SATA and is a standard for connecting
and transferring data from hard disk drives (HDDs) to computer systems.
Functions: Used to connect hard disk to host system like
computer motherboard.
 |
| Diagram 8: SATA Cable. |
Master/slave
Definition: Master/slave is a model of communication for
hardware devices where one device has a unidirectional control over one or more
devices.
Functions: This is often used in the electronic hardware
space where one device acts as the controller, whereas the other devices are
the ones being controlled. In short, one is the master and the others are
slaves to be controlled by the master.
Internal system unit: Ports
USB
Definition: Universal Serial Bus
is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables and
connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply between
computers, peripherals and another computer.
Functions: USB ports allow USB devices
to be connected to each other with and transfer digital data over USB cables.
They can also supply electric power across the cable to devices that need it.
 |
| Diagram 9: USB 3.0 Ports. |
Definition: It means two or more line that goes in the same
direction & same length. It can be found in the back of the computer and
also it`s part of the motherboard.
They are a 25-pin connector (type DB-25) that are used to
connect printers, computers and any other devices that may need a high
bandwidth. It is as known as a Centronics interface and now days ports are
developed by Epson.
Functions: To transmit multiple data streams in one time and
sends multiple of bits in a parallel data transmission in a fashion way.
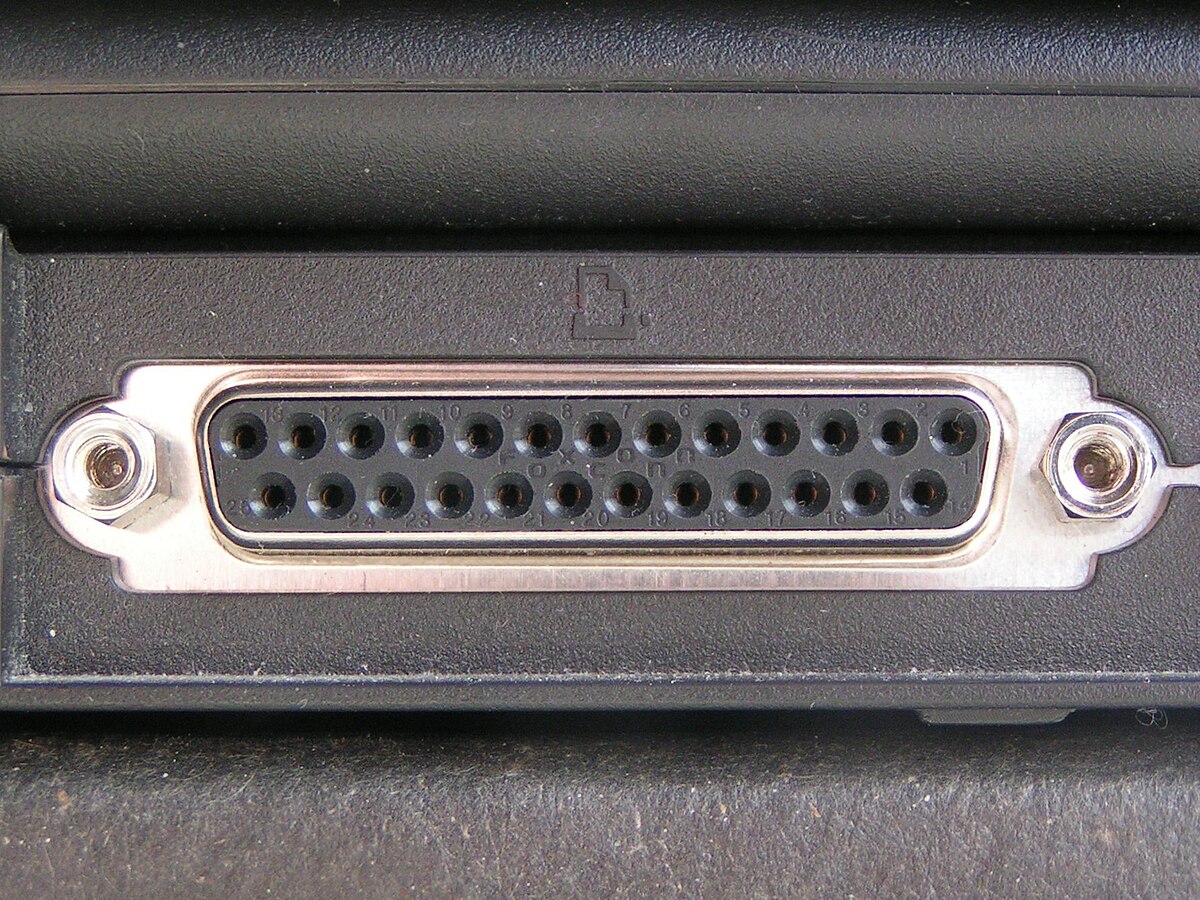 |
| Diagram 10: Parallel Port |
Internal system unit: Internal Memory
RAM.
Definition: It is a Random-Access Memory.
Functions: It is a
hardware device that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a
computer. RAM is a volatile memory and requires power to keep the data
accessible. If the computer is turned off, all data contained in RAM is lost.
 |
| Diagram 11: Random Access Memory (RAM) |
ROM
Definition: read-only memory, or ROM, stores information
that can only be read.
Functions: Any information stored in a ROM chip can only be
read and can hardly be edited. data will be intact even after switching off the
device or when the power supply is disconnected unexpectedly. ROM stores crucial
programs needed during booting.
/Amiga_1200_Kickstart_3.0_ROMs-56b429575f9b5829f82c66bd.jpg) |
| Diagram 12: Read Only Memory: ROM |
Cache
Definition: Cache memory is a chip-based computer component
that makes retrieving data from the computer's memory more efficient
Functions: to store program instructions that are
frequently re-referenced by software during operation. It is also to
speed up the working mechanism of computer.
 |
| Diagram 13: Cache |
Internal system unit: Specialized Card
Graphics Card:
Definition: Graphics cards is a hardware device that plug
into the motherboard and enables the computer to display images on the monitor.
A Graphics Card is a piece of computer hardware that produces the image you
see on a monitor.
Functions: Graphics cards allow computers to produce
graphics and images more quickly. A graphics card has its own processor, a GPU
(graphical processing unit).
The video card connects to the motherboard through PCI-E and
the monitor. This allows the card to accept information from the CPU (central
processing unit) and send output to the monitor.
 |
| Diagram 14: Graphics Card. |
Definition: It is a device installed on a computer for enabling it
to connect to a computer network.
Functions:
a NIC card can transmit signals at the physical layer and deliver data packets
at the network layer. it acts as a middleman between a
computer/server and a data network. When a user requests a web page, the LAN
card gets data from the user device, and sends them to the server on the
internet, then receives the required data back from the Internet to display for
users.
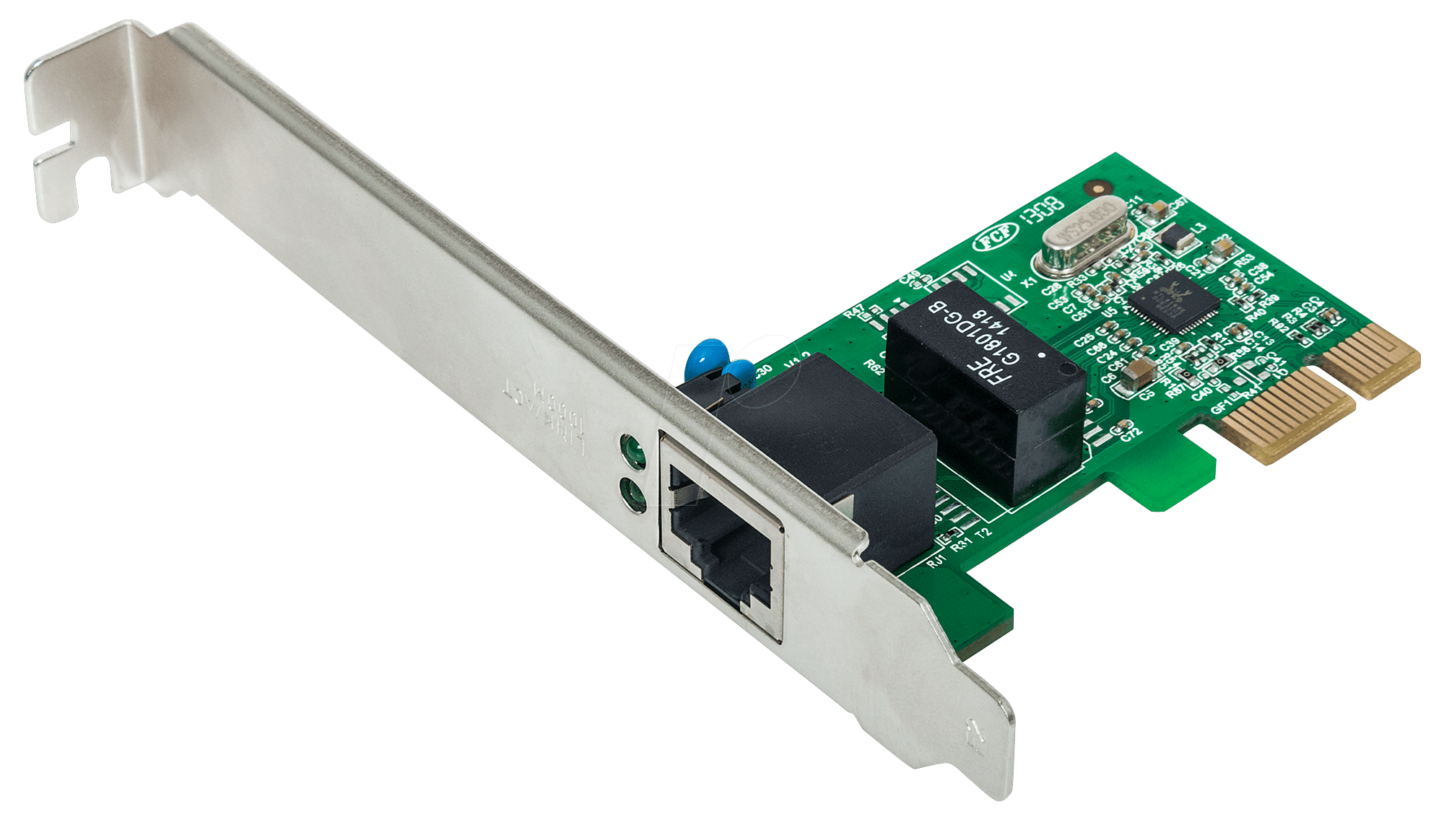 |
| Diagram 15: Network Card |
Peripherals: Monitor (Output Devices)
Definition: it is an electronic visual computer display
which is include of the screen, circuits, and also the case for to closed the
circuit. Or known as the visual display unit (VDU) or Video Display Terminal
(VDT).
Functions: the uses
of computer monitor are to displaying the output into a pictorial form that the
user can be more readable and understandable to the users. This will include
the various matrices like measure the performance of the computer monitors.
Like Aspect ratio, Display resolution, refresh rate, response
time etc.
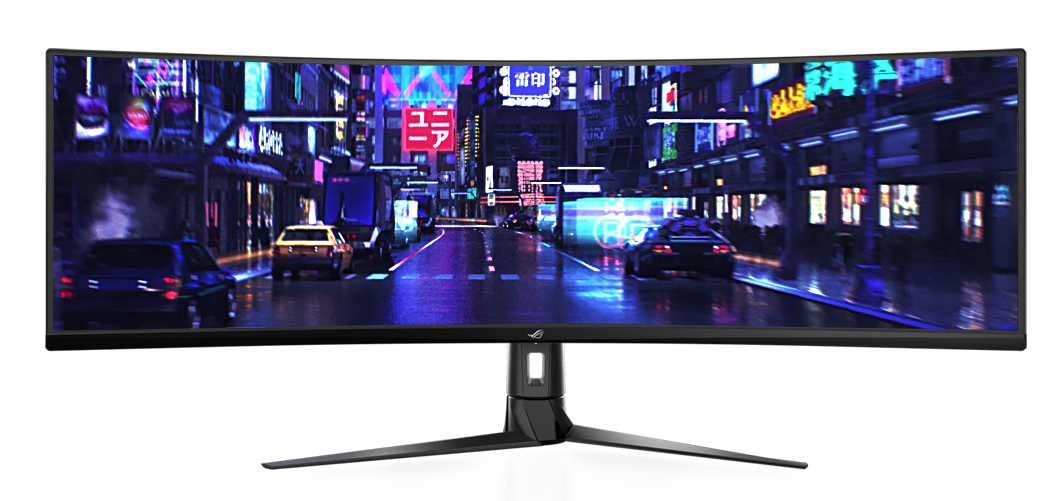 |
| Diagram 16: Monitor |
Peripherals: Printer (Output Devices)
Definition: It is a piece of hardware that takes the
electronic data which is stored on a computer that is generates a hard copy of
it. For example, to print the documents.
Functions: to print the documents such as:
1.
Color, Black and White print
2.
Scan, fax, copy, double side print.
3.
Photo printing, card printing, label printing,
envelop printing.
4.
legal-size paper printing, as well as almost
every size which would be used in daily life and work.
 |
| Diagram 17: Printer |
Peripherals: Plotter (Output Devices)
Definition: A plotter is a computer hardware device much like a printer that is used for printing vector graphics.
Functions: to produce hard copies of large graphs and
designs on paper, such as construction maps, engineering drawings,
architectural plans and business charts.
 |
| Diagram 18: Plotter |
Peripherals: Input Devices
Camera
Definition: it is a small digital video camera directly or
indirectly connected to a computer or a computer network.
Functions: It is used to perform video chat with another
person over the internet.
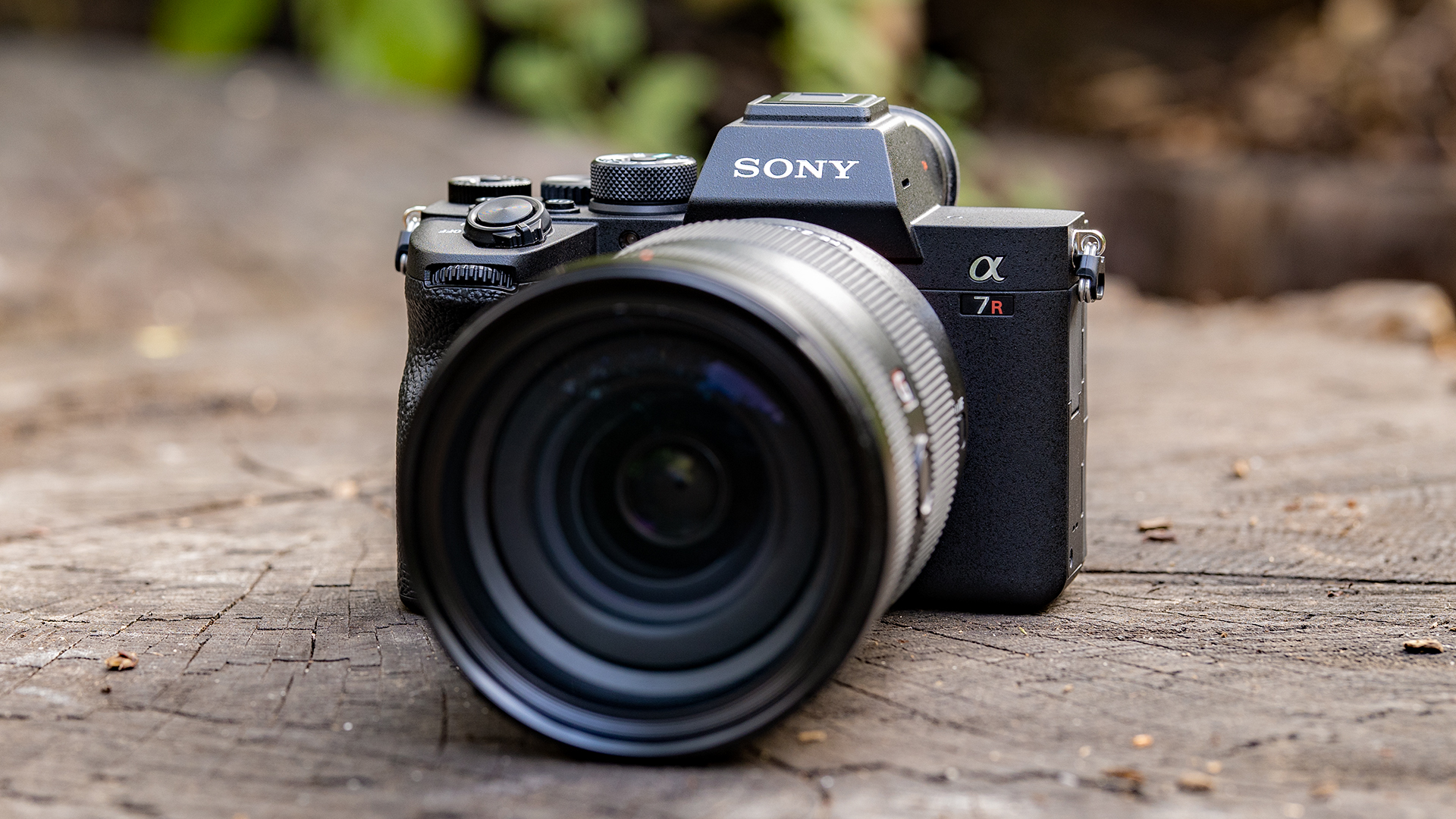 |
| Diagram 19: Camera |
Definition: A scanner is an input device that scans documents
such as photographs and pages of text. When a document is scanned, it is
converted into a digital format. This creates an electronic version of the
document that can be viewed and edited on a computer.
Functions:
1.
Sending Scanned files (Network Scanner)
2.
Scanning originals from a client computer (TWAIN
Scanner)
3.
Storing Files.
 |
| Diagram 20: Scanner |
Peripherals: Cabling
Coaxial
Definition: It is a type that using a
copper built with a metal shield and other types of the components to match it
with specialized of engineered to make block signal interference. This cable
has a plastic covering outside that is contain 2 parallel conductors which has
insulation cover protection. The coaxial cable has in two modes.
Functions: It is used as a transmission line
for radio frequency signals. Its applications include feedlines connecting
radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas, computer network (e.g.,
Ethernet) connections, digital audio (S/PDIF), and distribution of cable
television signals
 |
| Diagram 21: Coaxial Cable |
Twisted Pair
Definition: 2 types of twisted pair.
STP : Shielded twisted pair is a copper
telephone wire that is used in business environment. This type of the cable consists
a special cover or the jacket that is to purpose of block the external
interference. Usually this kind of wire are used for the fast data rate
Ethernet of voice and the data channels of telephone lines.
UTP: Unshielded twist pair (UTP) is a cable
that is used in a telecommunication even in computers that is using a cable.
With this type of cable, it has an ability to block interference which is not
too much depend on the physical shield. Mostly it is used as for the telephone’s
application.
 |
| Diagram 22: Twisated Pair. |
Optical fibre Optics
Definition: An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent
strand of very pure glass that acts as a light pipe to transmit light between
two ends of the fiber. It is used as a medium for telecommunication and
networking.
Functions: for the internet and computer networking.
 |
| Diagram 23: optical Fibre |
Backing Storages: Pen drives
Definition: A pen drive, or a USB flash drive, is a portable
data-storage device.
Functions of pen drive: A pen drive plugged into a USB port
can be used as an interfacing device to transfer files, documents and photos to
a PC. Similarly, select files can be transferred from a pen drive to any
workstation.
 |
| Diagram 24: pen drive |
Backing Storages: Optical Media
Definition: a data storage device or equipment that uses
optical data storage and retrieval techniques to read and write data. It stores
data digitally on a media device and uses a laser to read data from it.
Functions of Optical Media: to access information on
different parts of the disk. For example, DVD, CD, Blu-ray etc
 |
| Diagram 25: Optical Media examples |
Backing Storages: Flash Memory Cards
Definition: It is a type of storage media that is often used
to store photos, videos, or other data in electronic devices.
Types of computer memory cards:
- CF
(CompactFlash)
- MicroSD
- MMC
- SD
Card
- SDHC
Card
- Smart
Media Card
- Sony
Memory Stick
- xD-Picture
Card
Functions: To store the data of the image, Videos, document
etc.
 |
| Diagram 26: Flash memory Cards |
Backing Storages: Portable Drives and Fixed Drives
Portable drives:
A portable hard-drive is one that is placed into a small
case along with some electronics that allow the hard-drive to be accessed using
a USB or similar connection.
Portable hard-drives allow very large amounts of data to be
transported from computer to computer.
 |
| Diagram 27: Portable Drives. |
Fixed Drive:
A hard-drive built into the case of a computer is known as
‘fixed’. Almost every computer has a fixed hard-drive.
Fixed hard-drives act as the main backing storage device for
almost all computers since they provide almost instant access to files (random
access and high access speeds)
 |
| Diagram 28: Fixed drives |
Performance Factors
Data Transfer rate
Definition: Data transfer rate is the speed of which data
can be transferred from one device to the next, this if often measured in
megabytes (million bits). some examples of data transferring are copying and
moving files etc.
Capacity: the maximum minimum amount that a computer or
other devices can store.
 |
| Diagram 29: the examples of the Performance factors on a CPU. |
THE COMMUNICATION BETWEEN OF THE HARDWARE COMPONENTS
 |
| The diagram shows the connection of the hardware. |
On this diagram. the Cpu shows that how it communicates with all the compnents hardware that is gathered together. As you can see on the diagram, If the CPU wanted to communicate with any of the components then it will go through the bus to transfer the data in order to reach the components.
References:
Definitions, N. and Hope, C.
Definitions, N. and Hope, C. (2020) What is NIC (Network Interface Card)?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/n/nic.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, M. and Hope, C.
Definitions, M. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Monitor?, Computerhope.com. Available at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/m/monitor.htm
(Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, P. and Hope, C.
Definitions, P. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Printer?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/printer.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, P. and Hope, C.
Definitions, P. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Plotter?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/plotter.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, C. and Hope, C.
Definitions, C. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Camera?, Computerhope.com.
Available at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/c/camera.htm (Accessed: 21
May 2020).
Definitions, O. and Hope, C.
Definitions, O. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Scanner?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/o/optiscan.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, C. and Hope, C.
Definitions, C. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Cable?, Computerhope.com.
Available at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/c/cable.htm (Accessed: 21 May
2020).
Definitions, B. and Hope, C.
Definitions, B. and Hope, C. (2020) What is Backing Storage?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/b/backing-storage.htm (Accessed: 21 May
2020).
Definitions, O. and Hope, C.
Definitions, O. and Hope, C. (2020) What is an Optical Disc?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/o/optidisc.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, M. and Hope, C.
Definitions, M. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Memory Card?, Computerhope.com. Available at:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/m/memocard.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
References:
What is a Processor? - Definition from Techopedia
What is a Processor? - Definition from Techopedia (2020). Available at: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/28254/processor (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
What is Processor (CPU) in Computer? | Gaming CPUs
What is Processor (CPU) in Computer? | Gaming CPUs (2019). Available at: https://gamingcpus.com/what-is-processor-cpu-in-computer (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Anon
(2020) Study.com. Available at: https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-a-motherboard-definition-function-diagram.html (Accessed: 21 May 2020)
It's the air traffic controller of the computer. The motherboard: Explained!
It's the air traffic controller of the computer. The motherboard: Explained! (2019). Available at: https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/what-is-a-motherboard/ (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, B. and Hope, C.
Definitions, B. and Hope, C. (2020) What is BIOS?, Computerhope.com. Available at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/b/bios.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, P. and Hope, C.
Definitions, P. and Hope, C. (2020) What is Power Supply?, Computerhope.com. Available at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/power-supply.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
HSF (Heat Sink and Fan) Definition
HSF (Heat Sink and Fan) Definition (2020). Available at: https://techterms.com/definition/hsf (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
What Is a Hard Drive? A Beginner's Guide
to Computer Storage | Digital Trends
What Is a
Hard Drive? A Beginner's Guide to Computer Storage | Digital Trends (2020).
Available at:
https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/what-is-a-hard-drive-your-guide-to-computer-storage/
(Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Difference Between IDE and EIDE | Difference
Between
Difference
Between IDE and EIDE | Difference Between (2020). Available at:
http://www.differencebetween.net/technology/difference-between-ide-and-eide/
(Accessed: 21 May 2020).
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology
Attachment) Definition
SATA (Serial
Advanced Technology Attachment) Definition (2020). Available at:
https://techterms.com/definition/sata (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
A USB Port Is One of the Most Useful
Features on Computers and Phones
A USB Port
Is One of the Most Useful Features on Computers and Phones (2020). Available
at: https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-a-usb-port-818166 (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Definitions, P. and Hope, C.
Definitions,
P. and Hope, C. (2020) What is a Parallel Port?, Computerhope.com. Available
at: https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/paraport.htm (Accessed: 21 May 2020).
Internal Memory
Internal
Memory (2020). Available at:
https://computerhardwarecomps.weebly.com/internal-memory.html (Accessed: 21 May
2020).
Comments
Post a Comment